Laboratory Electrophoresis Units
Manufacturer for Electrophoresis Units
Electrophoresis equipment for a wide range of applications
Electrophoresissystems are devices that find their application mainly in laboratories of molecular biology, biochemistry, biotechnology, food analysis, veterinary and human medicine.
The main applications of electrophoresis equipment include the preparation of polyacrylamide gels, electrophoretic separation of proteins, nucleic acids, protein staining, DNA / RNA analysis in the form of fragments and DNA sequencing in the laboratory. Electrophoresis is a laboratory technique in which mixtures of substances or particles are separated in an electric field on the basis of size, weight and electric charge.
In laboratory medicine, for example, serum electrophoresis is used for the electrophoretic fractionation of serum proteins. By means of protein electrophoresis, physicians obtain information about the occurrence of the relative quantity of the proteins albumin, alpha-1-, alpha-2- and beta-globulin as well as gamma-globulin in the blood for the diagnosis of various diseases.
The electrophoresis equipment offered by the manufacturers Elettrofor and BIOTEC FISCHER is primarily suitable for various gel applications and experiments in the laboratory.
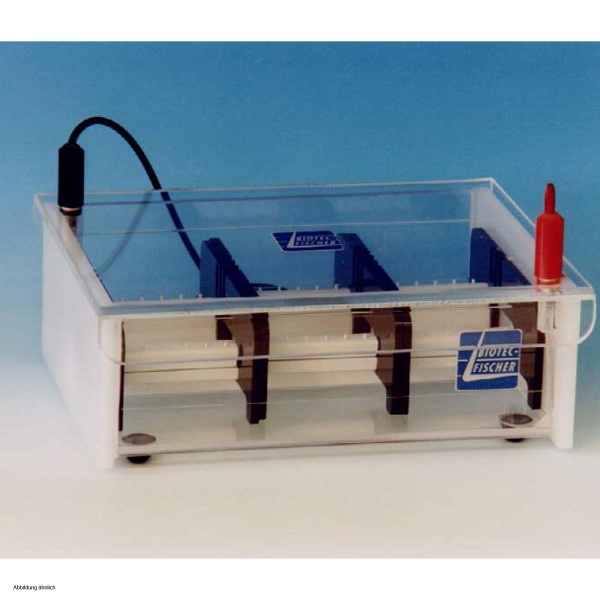
Gel electrophoresis equipment - functional principle
Gel electrophoresis systems are laboratory devices used in the laboratory for gel electrophoresis, a procedure in which a gel is used as a carrier medium. Agarose or polyacrylamide form a close-meshed network in the compound, which slows down the molecules to be separated as they migrate [migrate] in the electric field.
The principle of gel electrophoresis
Here, electrophoresis works by electrophoretically separating through the pores present in the gel, which act like a sieve and whose size determines the speed of migration of molecules present in the gel. Depending on the size and charge of the molecules, they move at different speeds through the gel, which acts as a molecular sieve. The size of the pores of the gel is determined by the concentration of the underlying gel, agarose or polyacrylamide.
Agarose gel
Agarose gels have large pores and the pore size can be controlled by the concentration of agarose. 1% gels have pore sizes around 150 nanometres , 0.15% gels around 500 nm. Agarose gel electrophoresis is suitable for the separation of DNA and larger protein molecules. The main application is the separation of nucleic acids.
Polyacrylamide gel
Polyacrylamide gels are produced by the polymerisation of acrylamide. They have much smaller pores between 3 and 6 nanometres. The pore size depends on acrylamide concentration as well as the degree of cross-linking. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is often used in the separation of smaller protein molecules.
Gel electrophoresis systems - types
Gel electrophoresis apparatuses come in different designs, sizes and models. Different gel electrophoresis systems are used depending on the type of electrophoresis, area of application, procedure, carrier material and other factors.
Classic gel electrophoresis is carried out as zone electrophoresis. Discontinuous electrophoresis is used to achieve a higher resolution. Furthermore, there are electrophoresis types such as free-flow electrophoresis, density gradient electrophoresis, capillary electrophoresis or affinity electrophoresis. We divide our gel electrophoresis instruments according to gel chambers: Agarose gel & polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis:
Electrophoresis systems: discover high-quality accessories at ProfiLab24.com
Depending on the electrophoresis system, you can order different components and electrophoresis equipment accessories such as different glass plates, electrophoresis chambers, combs, gel carriers, gel casting systems, gel casting ramps, spacer sets, contrast plates - and other accessories for the offered gel electrophoresis systems.
Do you have questions about a specific device or are you looking for the right accessories? Then do not hesitate to contact us. You can reach us by phone at +49 30 403 667 940 or by e-mail at [email protected] - We look forward to hearing from you!